領先一步
VMware 提供培訓和認證,助您加速進步。
瞭解更多在最近的一篇研究論文《構建高效代理》中,Anthropic 分享了關於構建高效大型語言模型 (LLM) 代理的寶貴見解。這項研究特別有趣的是,它強調了簡單性和可組合性,而非複雜的框架。讓我們探討一下這些原則如何使用 Spring AI 轉化為實際實現。
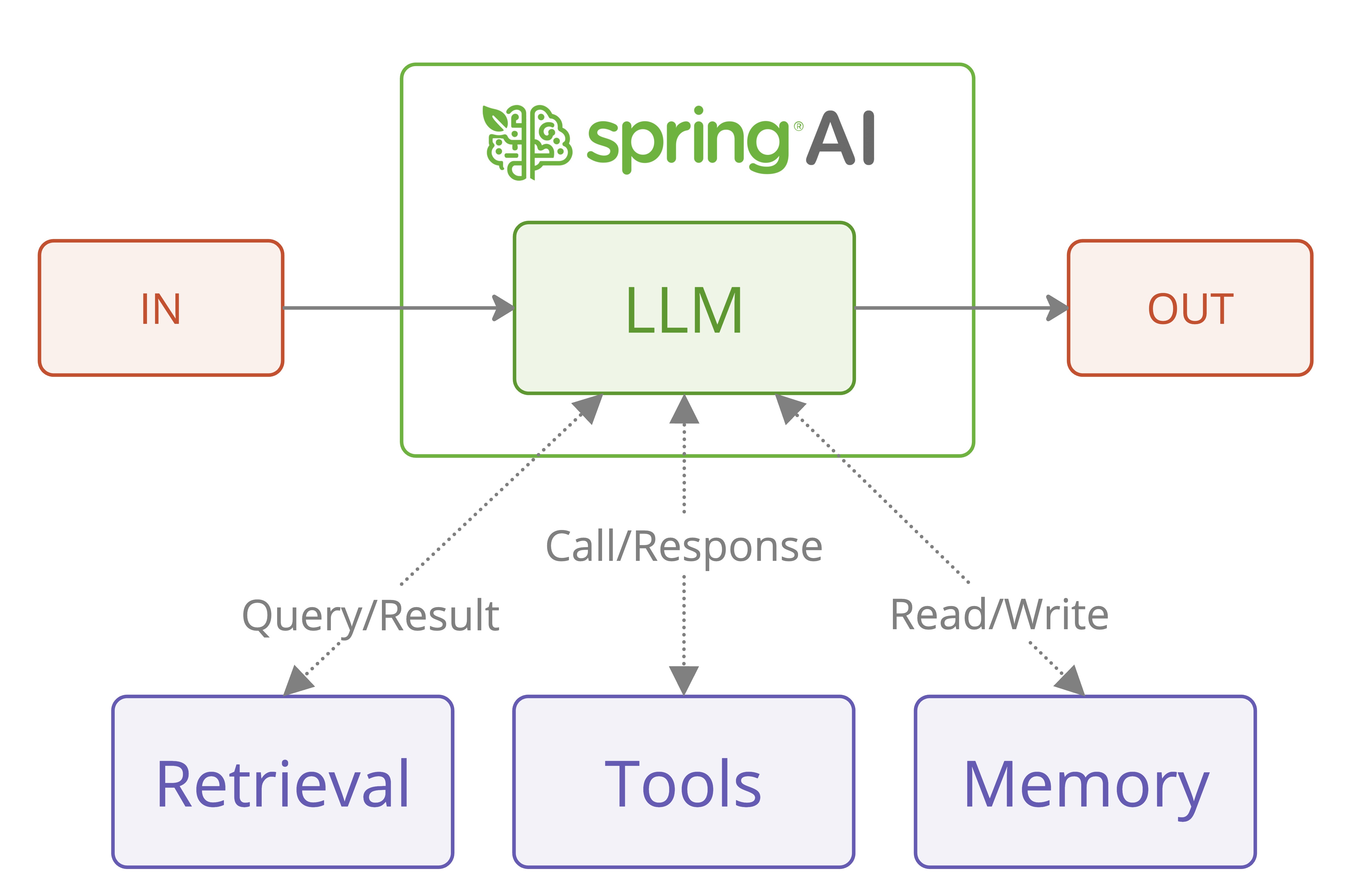
雖然模式描述和圖表來源於 Anthropic 的原始出版物,但我們將重點介紹如何使用 Spring AI 的特性來實現這些模式,以實現模型可移植性和結構化輸出。我們建議首先閱讀原始論文。
agentic-patterns 專案實現了下面討論的模式。
這項研究出版物在兩種型別的代理系統之間做出了重要的架構區分:
關鍵的見解是,雖然完全自主的代理可能看起來很有吸引力,但工作流通常為明確定義的任務提供更好的可預測性和一致性。這與對可靠性和可維護性至關重要的企業要求完美契合。
讓我們透過五種基本模式來研究 Spring AI 如何實現這些概念,每種模式都服務於特定的用例:
鏈式工作流模式是分解複雜任務為更簡單、更易管理步驟的原則的典範。
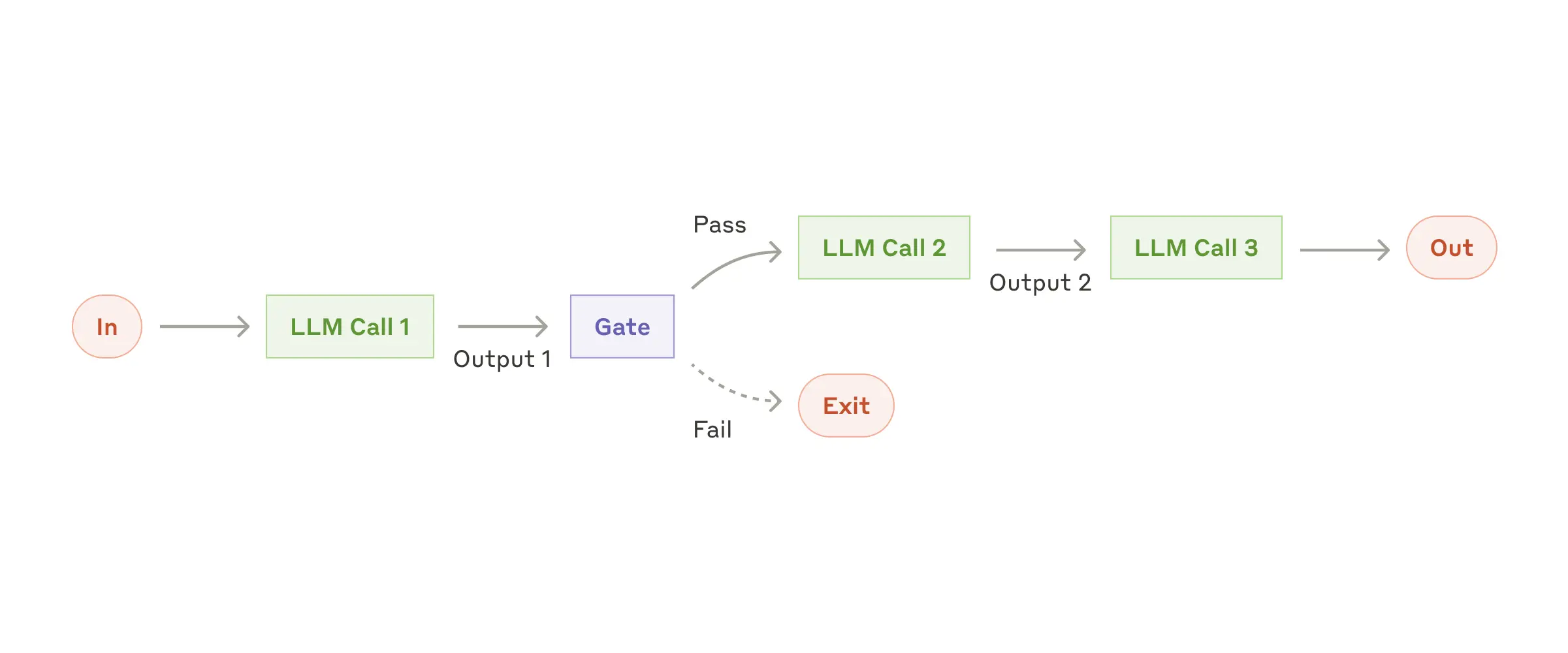
何時使用
以下是 Spring AI 實現中的一個實際示例:
public class ChainWorkflow {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
private final String[] systemPrompts;
// Processes input through a series of prompts, where each step's output
// becomes input for the next step in the chain.
public String chain(String userInput) {
String response = userInput;
for (String prompt : systemPrompts) {
// Combine the system prompt with previous response
String input = String.format("{%s}\n {%s}", prompt, response);
// Process through the LLM and capture output
response = chatClient.prompt(input).call().content();
}
return response;
}
}
此實現演示了幾個關鍵原則:
LLM 可以同時處理任務,並以程式設計方式聚合其輸出。並行化工作流以兩種主要變體體現:
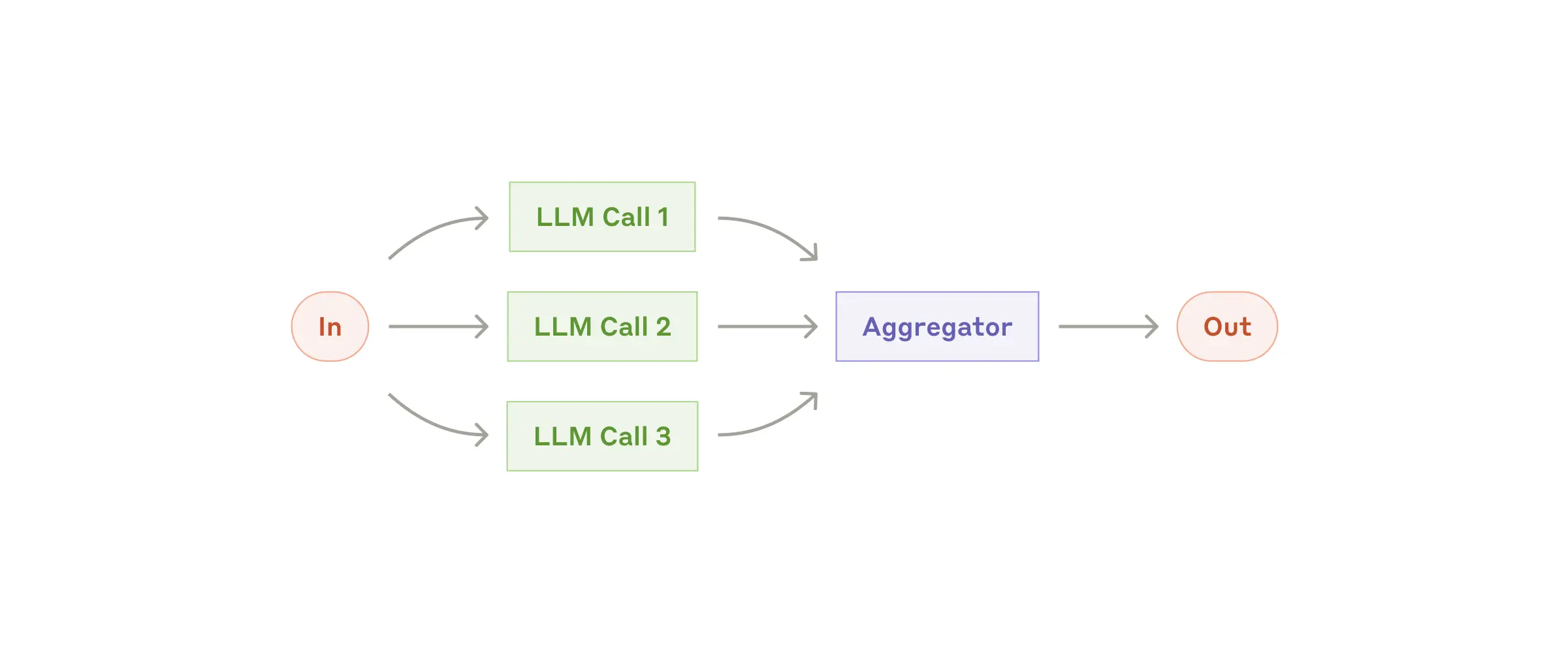
何時使用
並行化工作流模式演示了多個大型語言模型(LLM)操作的高效併發處理。此模式特別適用於需要並行執行 LLM 呼叫並自動聚合輸出的場景。
以下是使用並行化工作流的基本示例:
List<String> parallelResponse = new ParallelizationWorkflow(chatClient)
.parallel(
"Analyze how market changes will impact this stakeholder group.",
List.of(
"Customers: ...",
"Employees: ...",
"Investors: ...",
"Suppliers: ..."
),
4
);
此示例演示了利益相關者分析的並行處理,其中每個利益相關者組都同時進行分析。
路由模式實現智慧任務分發,為不同型別的輸入提供專門的處理。
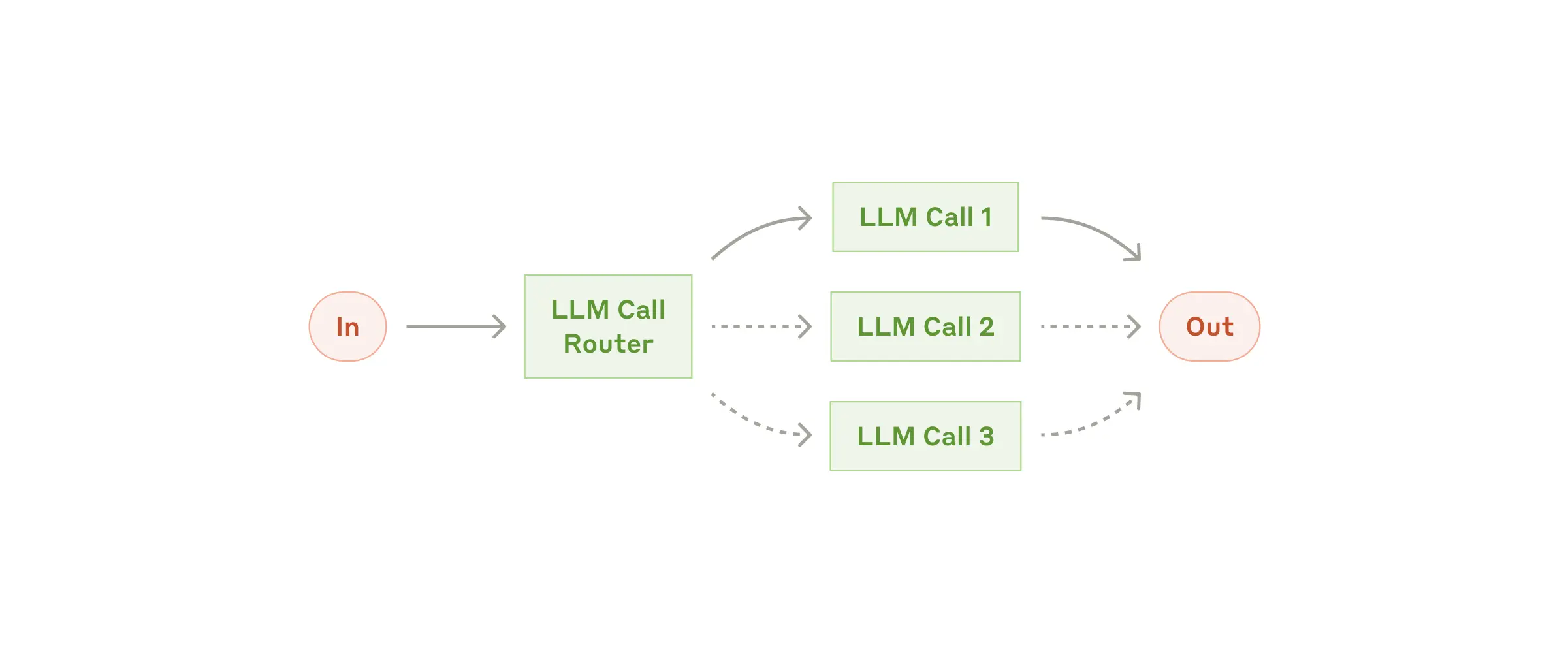
此模式專為複雜任務而設計,其中不同型別的輸入透過專門的流程進行更好地處理。它使用 LLM 分析輸入內容並將其路由到最合適的專門提示或處理程式。
何時使用
以下是使用路由工作流的基本示例:
@Autowired
private ChatClient chatClient;
// Create the workflow
RoutingWorkflow workflow = new RoutingWorkflow(chatClient);
// Define specialized prompts for different types of input
Map<String, String> routes = Map.of(
"billing", "You are a billing specialist. Help resolve billing issues...",
"technical", "You are a technical support engineer. Help solve technical problems...",
"general", "You are a customer service representative. Help with general inquiries..."
);
// Process input
String input = "My account was charged twice last week";
String response = workflow.route(input, routes);
此模式演示瞭如何在保持控制的同時實現更復雜的代理類行為
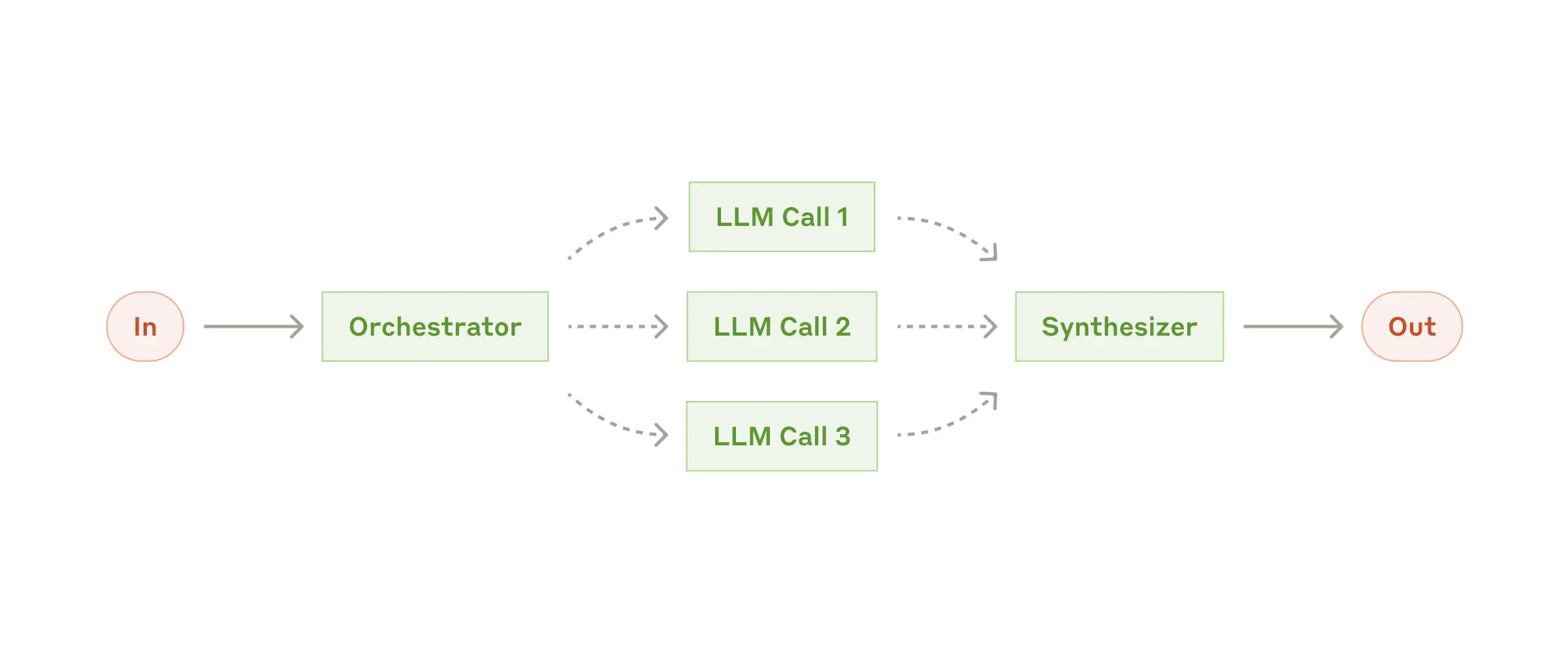
何時使用
該實現使用 Spring AI 的 ChatClient 進行 LLM 互動,幷包括
public class OrchestratorWorkersWorkflow {
public WorkerResponse process(String taskDescription) {
// 1. Orchestrator analyzes task and determines subtasks
OrchestratorResponse orchestratorResponse = // ...
// 2. Workers process subtasks in parallel
List<String> workerResponses = // ...
// 3. Results are combined into final response
return new WorkerResponse(/*...*/);
}
}
ChatClient chatClient = // ... initialize chat client
OrchestratorWorkersWorkflow workflow = new OrchestratorWorkersWorkflow(chatClient);
// Process a task
WorkerResponse response = workflow.process(
"Generate both technical and user-friendly documentation for a REST API endpoint"
);
// Access results
System.out.println("Analysis: " + response.analysis());
System.out.println("Worker Outputs: " + response.workerResponses());
評估器-最佳化器模式實現了一個雙 LLM 過程,其中一個模型生成響應,而另一個模型在迭代迴圈中提供評估和反饋,類似於人類作者的精煉過程。該模式由兩個主要元件組成:
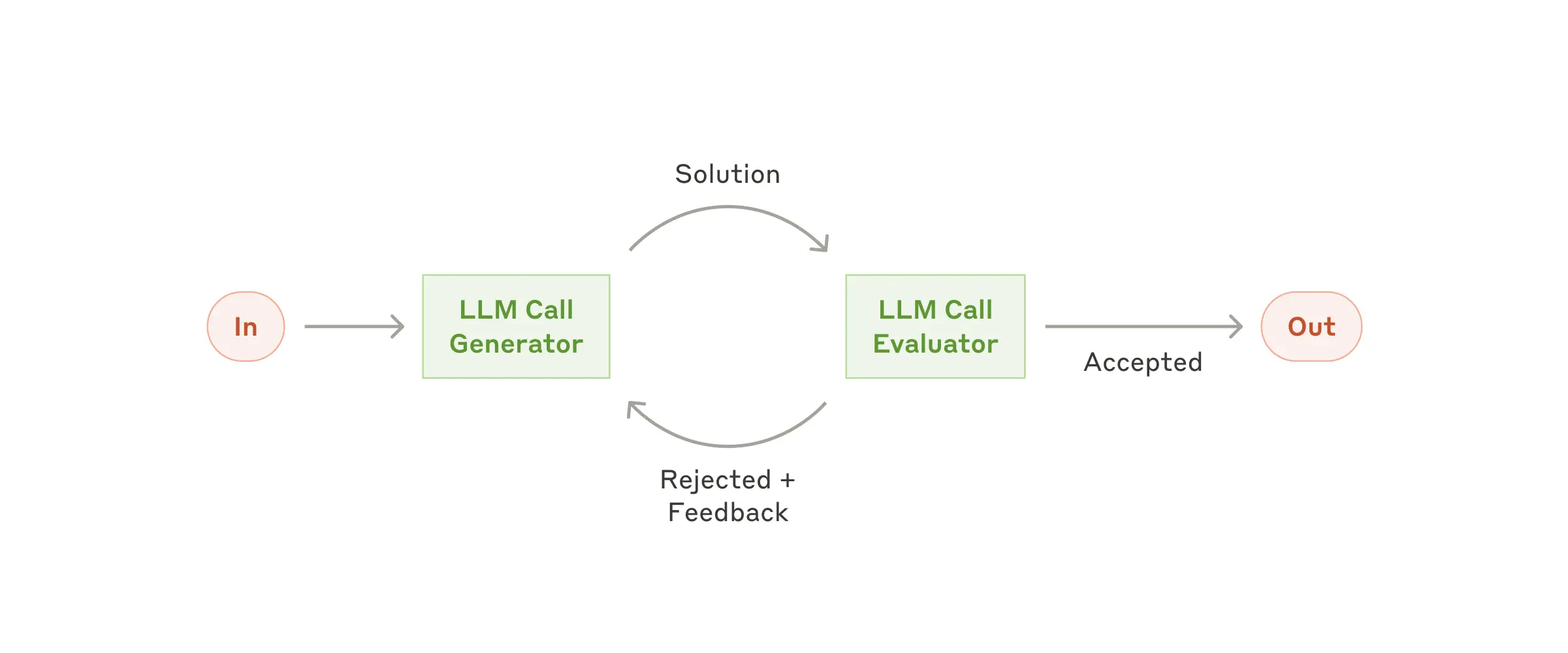
何時使用
該實現使用 Spring AI 的 ChatClient 進行 LLM 互動,幷包括
public class EvaluatorOptimizerWorkflow {
public RefinedResponse loop(String task) {
// 1. Generate initial solution
Generation generation = generate(task, context);
// 2. Evaluate the solution
EvaluationResponse evaluation = evaluate(generation.response(), task);
// 3. If PASS, return solution
// 4. If NEEDS_IMPROVEMENT, incorporate feedback and generate new solution
// 5. Repeat until satisfactory
return new RefinedResponse(finalSolution, chainOfThought);
}
}
ChatClient chatClient = // ... initialize chat client
EvaluatorOptimizerWorkflow workflow = new EvaluatorOptimizerWorkflow(chatClient);
// Process a task
RefinedResponse response = workflow.loop(
"Create a Java class implementing a thread-safe counter"
);
// Access results
System.out.println("Final Solution: " + response.solution());
System.out.println("Evolution: " + response.chainOfThought());
Spring AI 對這些模式的實現提供了與 Anthropic 建議相符的幾項優勢:
<!-- Easy model switching through dependencies -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-openai-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
// Type-safe handling of LLM responses
EvaluationResponse response = chatClient.prompt(prompt)
.call()
.entity(EvaluationResponse.class);
基於 Anthropic 的研究和 Spring AI 的實現,以下是構建基於 LLM 的有效系統的關鍵建議:
從簡單開始
設計可靠性
考慮權衡
在本系列的第 2 部分中,我們將探討如何構建更高階的代理,將這些基礎模式與複雜功能結合起來:
模式組合
高階代理記憶體管理
工具和模型上下文協議 (MCP) 整合
敬請關注這些高階功能的詳細實現和最佳實踐。
VMware Tanzu Platform 10 Tanzu AI Server,由 Spring AI 提供支援,提供:
有關使用 Tanzu AI Server 部署 AI 應用程式的更多資訊,請訪問 VMware Tanzu AI 文件。
Anthropic 的研究洞察與 Spring AI 的實際實現相結合,為構建基於 LLM 的有效系統提供了強大的框架。透過遵循這些模式和原則,開發人員可以建立健壯、可維護和有效的 AI 應用程式,在避免不必要的複雜性的同時提供真正的價值。
關鍵是記住,有時最簡單的解決方案最有效。從基本模式開始,徹底理解您的用例,並且僅在可證明地提高系統性能或功能時才增加複雜性。