領先一步
VMware 提供培訓和認證,助您加速進步。
瞭解更多開發、部署和操作雲應用程式應該像本地應用程式一樣容易(甚至更容易)。這是並且應該成為任何雲平臺、庫或工具的指導原則。Spring Cloud——一個開源庫——使得為雲開發 JVM 應用程式變得容易。有了它,應用程式可以輕鬆地連線到服務並發現多個雲(如 Cloud Foundry 和 Heroku)中的雲環境資訊。此外,您可以將其擴充套件到其他雲平臺和新服務。
在這篇部落格(系列文章中的第一篇)中,我將介紹 Spring Cloud,並從應用開發者的角度展示其用法。我們將開發一個簡單的應用程式,並將其部署到 Cloud Foundry 和 Heroku。在後續的部落格中,我將探討其可擴充套件性。
在雲中執行應用程式的眾多優勢之一是,可以輕鬆獲取各種服務。您無需管理硬體、安裝、操作、備份等,只需點選按鈕或使用 shell 命令即可建立和繫結服務。
應用程式如何訪問這些服務?例如,如果您的應用程式綁定了關係資料庫,則需要根據該服務建立 DataSource 物件。這就是 Spring Cloud 幫助的地方。它消除了訪問和配置服務聯結器所需的所有工作,讓您專注於使用這些服務。它還公開了應用程式例項資訊(主機地址、埠、名稱等)。
Spring Cloud 透過雲聯結器(Cloud Connector)的概念,以一種與雲無關的方式完成所有這些工作。雖然它提供了 Cloud Foundry 和 Heroku 的實現,但您(或雲提供商)可以透過實現介面並利用庫的其餘部分來將其擴充套件到其他雲。然後,只需將包含擴充套件的庫新增到應用程式的類路徑中;無需分叉和構建 Spring Cloud。
Spring Cloud 也認識到它不可能滿足每個雲上的所有服務。因此,在開箱即用支援許多常見服務的同時,它允許您(或服務提供商)將其功能擴充套件到其他服務。就像為其他雲擴充套件一樣,您將包含服務擴充套件的 jar 新增到應用程式的類路徑中。
最後,它為 Spring 應用程式(在一個單獨的模組中)提供了特殊支援,包括 Spring Boot 應用程式,形式包括 Java 和 XML 配置支援,並以易於使用的方式公開應用程式和服務屬性。這是 Spring Cloud 中唯一依賴 Spring 的模組。其他框架提供商可以以類似的方式為其框架貢獻特定支援。
讓我們看看 Spring Cloud 的實際應用。
我們將從一個基於 Spring Boot 的簡單應用程式(原始碼)開始(傳統的 Spring MVC 應用程式也可以正常工作,儘管需要更多的設定程式碼)。該應用程式包含一個控制器,其中注入了表示繫結服務的 bean,以及一個主頁,用於列印有關繫結到應用程式的服務的資訊。
@Controller
public class HomeController {
@Autowired(required = false) DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired(required = false) RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory;
@Autowired(required = false) MongoDbFactory mongoDbFactory;
@Autowired(required = false) ConnectionFactory rabbitConnectionFactory;
@Autowired ApplicationInstanceInfo instanceInfo;
@RequestMapping("/")
public String home(Model model) {
Map<Class<?>, String> services = new LinkedHashMap<Class<?>, String>();
services.put(dataSource.getClass(), toString(dataSource));
services.put(mongoDbFactory.getClass(), toString(mongoDbFactory));
services.put(redisConnectionFactory.getClass(), toString(redisConnectionFactory));
services.put(rabbitConnectionFactory.getClass(), toString(rabbitConnectionFactory));
model.addAttribute("services", services.entrySet());
model.addAttribute("instanceInfo", instanceInfo);
return "home";
}
// ... various toString() methods to create a string representation for each service
}
HomeController 有四個注入的依賴項,表示可以繫結到應用程式的服務,還有一個用於 ApplicationInstanceInfo。“/” 路由將表示每個服務及其類的字串以及例項資訊新增到模型中。相關檢視 呈現所有這些資訊。
對於配置,我們新增 CloudConfig,如下所示
@Configuration
@ServiceScan
@Profile("cloud")
public class CloudConfig extends AbstractCloudConfig {
@Bean
public ApplicationInstanceInfo applicationInfo() {
return cloud().getApplicationInstanceInfo();
}
}
該類擴充套件了 AbstractCloudConfig,這是使用 Spring Cloud 的 Java 配置方法。我們設定 @Profile(“cloud”) 以確保此配置僅在雲環境中載入。@ServiceScan 註解掃描所有繫結服務併為每個服務建立一個 bean(然後自動裝配到 HomeController 中)。如果您對 @ComponentScan 和 @ServiceScan 之間的並行關係感到好奇,那麼您是正確的。前者掃描可以例項化為 bean 的候選類,而後者掃描繫結服務。我們還建立了一個與應用程式例項資訊對應的 bean。
我們包含以下 manifest.yml,它綁定了我們用於演示目的所需的所有四個服務(您需要使用 cf create-service 命令建立這些服務)
---
applications:
- name: hello-spring-cloud
memory: 512M
instances: 1
host: hello-spring-cloud-${random-word}
domain: cfapps.io
path: target/hello-spring-cloud-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
services:
- postgres-service
- amqp-service
- mongodb-service
- redis-service
env:
SPRING_PROFILES_DEFAULT: cloud
現在我們所要做的就是構建和推送
$ mvn package
$ cf push
```
Now when we visit the page, we see information about all four services:
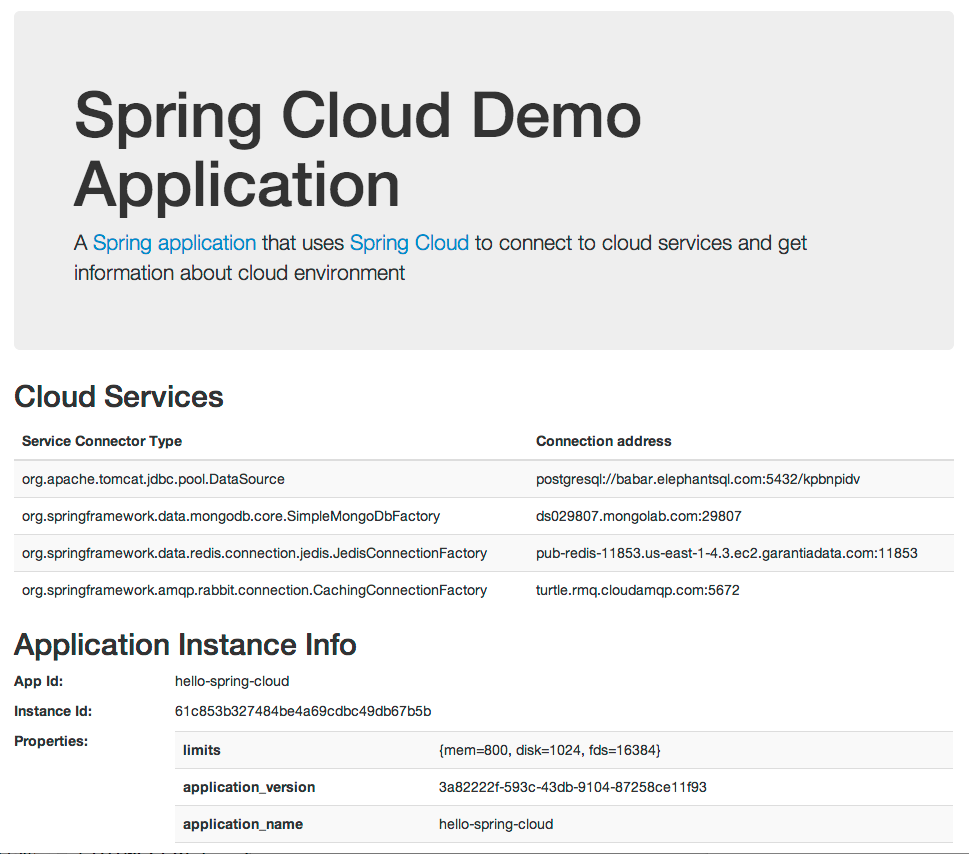
In a real app, you probably would inject these services into service beans and do something more useful that printing their connection information! Please head over to http://projects.spring.io/spring-cloud to see a list of sample apps that do more interesting things with Spring Cloud. Speaking of https://springframework.tw, it too uses Spring Cloud underneath.
# Deploying it to Heroku
We can deploy the same application to Heroku. We need to add a couple of files (neither are specific to Spring Cloud): `system.properties` to make Heroku use Java 7 and `Procfile` to make it execute the right command to start the application and enable the `cloud` profile. We push the application to Heroku as follows:
```sh
$ heroku apps:create
$ heroku addons:add mongolab
$ heroku addons:add rediscloud
$ heroku addons:add cloudamqp
$ heroku config:set SPRING_CLOUD_APP_NAME=hello-spring-cloud
$ git push heroku master
```
Here we create add-ons (similar to Cloud Foundry services) for a MongoDb, Redis, and AMQP service provider. Heroku automatically provisions a Postgres service, therefore we don’t need to explicitly add it. Heroku app’s environment, unlike Cloud Foundry, doesn’t expose the app name, so we use `heroku config:set` to explicitly set it (if not, Spring Cloud will set it to `<unknown>`). There are a few other differences in how Spring Cloud adapts to differences between these two clouds; we will cover those in a later blog.
That’s all we need to do. When we visit our application, it shows all services info much the same way it did on Cloud Foundry.
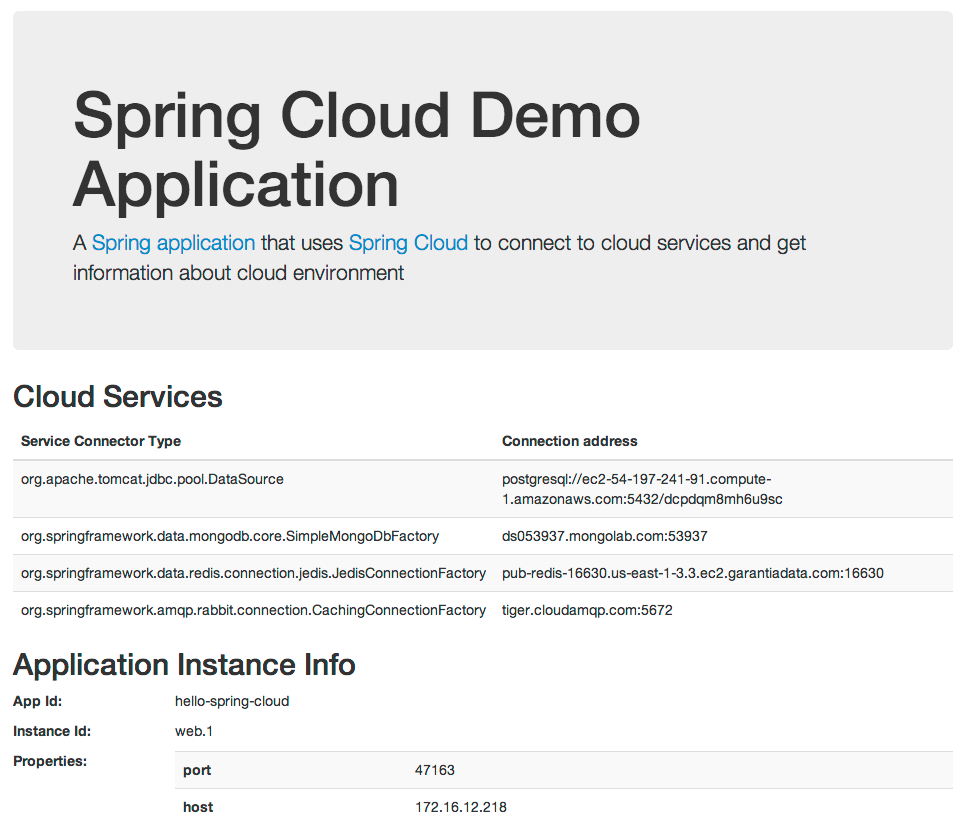
# Taking some control
The use of `@ServiceScan` made it easy to grab all services and start using them. But in practice, you often need more control over creating a service connector such as setting their pooling parameters. If that is the case, you can use Spring Cloud’s Java Config or XML config support. Let’s change the `CloudConfig` class as follows:
```java
@Configuration
@Profile("cloud")
public class CloudConfig extends AbstractCloudConfig {
@Bean
public ConnectionFactory rabbitConnectionFactory() {
return connectionFactory().rabbitConnectionFactory();
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
return connectionFactory().dataSource();
}
@Bean
public MongoDbFactory mongoDb() {
return connectionFactory().mongoDbFactory();
}
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
return connectionFactory().redisConnectionFactory();
}
@Bean
public ApplicationInstanceInfo applicationInfo() {
return cloud().getApplicationInstanceInfo();
}
}
```
Compared to the first version, we removed the `@ServiceScan` annotation. Instead, we use the API exposed by `AbstractCloudConfig` to create beans for each of the services. For now, the beans created this way are identical to that created by `@ServiceScan`, but we now have a possibility of configuring it further. For example, if we wanted to bind the `DataSource` bean to a specific service (presumably among many bound to the app) and initialize it with a specific pool configuration, we can make the following change:
```java
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
PoolConfig poolConfig = new PoolConfig(20, 200);
ConnectionConfig connectionConfig =
new ConnectionConfig("sessionVariables=sql_mode='ANSI';characterEncoding=UTF-8");
DataSourceConfig serviceConfig =
new DataSourceConfig(poolConfig, connectionConfig);
return connectionFactory().dataSource("my-service", serviceConfig);
}
```
The `DataSource` created this way will have max pool size of 20 and max wait time of 200 milliseconds along with a specific connection property string.
# Summary
Spring Cloud abstracts connecting to cloud services and makes it possible to have the same application deployed to multiple clouds with little extra effort. In this blog we merely scratched the surface of what Spring Cloud offers. In the next blog, we will explore more about the Java and XML config as well as how you can use its core API in non-spring apps. In the blogs that follow we will dive deeper into the extensibility angle of Spring Cloud.